The 26,000-Year Astronomical Monument Hidden in Plain Sight
The western flank of the Hoover Dam holds a celestial map that marks the time of the dam’s creation based on the 25,772-year axial precession of the earth.

On the western flank of the Hoover Dam stands a little-understood monument, commissioned by the US Bureau of Reclamation when construction of the dam began in 01931. The most noticeable parts of this corner of the dam, now known as Monument Plaza, are the massive winged bronze sculptures and central flagpole which are often photographed by visitors. The most amazing feature of this plaza, however, is under their feet as they take those pictures.
The plaza’s terrazzo floor is actually a celestial map that marks the time of the dam’s creation based on the 25,772-year axial precession of the earth.

I was particularly interested in this monument because this axial precession is also the slowest cycle that we track in Long Now’s 10,000 Year Clock. Strangely, little to no documentation of this installation seemed to be available, except for a few vacation pictures on Flickr. So the last time I was in Las Vegas, I made a special trip out to Hoover Dam to see if I could learn more about this obscure 26,000-year monument.
I parked my rental car on the Nevada side of the dam on a day pushing 100 degrees. I quickly found Monument Plaza just opposite the visitor center where tours of the dam are offered. While the plaza is easy to find, it stands apart from all the main tours and stories about the dam. With the exception of the writing in the plaza floor itself, the only information I could find came from a speaker running on loop, broadcasting a basic description of the monument while visitors walked around the area. When I asked my tour guide about it, he suggested that there may be some historical documentation and directed me to Emme Woodward, the dam’s historian.


I was able to get in touch with her after returning home. As she sent me a few items, I began to see why the Bureau of Reclamation doesn’t explain very much about the monument’s background. The first thing she sent me was a description of the plaza by Oskar J. W. Hansen, the artist himself, which I thought would tell me everything I wanted to know. While parts of it were helpful, the artist’s statement of intention was also highly convoluted and opaque. An excerpt:
These [human] postures may be matched to their corresponding reflexes in terms of angle and degree much as one would join cams in a worm-gear drive. There is an angle for doubt, for sorrow, for hate, for joy, for contemplation, and for devotion. There are as many others as there are fleeting emotions within the brain of each individual who inhabits the Earth. Who knows not all these postures of the mind if he would but stop to think of them as usable factors for determining proclivities of character? It is a knowledge bred down to us through the past experience of the whole race of men.
It is pretty hard to imagine the US Bureau of Reclamation using this type of write-up to interpret the monument… and they don’t. And so there it stands, a 26,000-year clock of sorts, for all the world to see, and yet still mired in obscurity.

While I may never totally understand the inner motivations of the monument’s designer, I did want to understand it on a technical level. How did Hansen create a celestial clock face frozen in time that we can interpret and understand as the date of the dam’s completion? The earth’s axial precession is a rather obscure piece of astronomy, and our understanding of it through history has been spotty at best. That this major engineering feat was celebrated through this monument to the axial precession still held great interest to me, and I wanted to understand it better.

I pressed for more documentation, and the historian sent me instructions for using the Bureau of Reclamation’s image archive site as well as some keywords to search for. The black and white images you see here come from this resource. Using the convoluted web site was a challenge, and at first I had difficulty finding any photos of the plaza before or during its construction. As I discovered, the problem was that I was searching with the term “Monument Plaza,” a name only given to it after its completion in 01936. In order to find images during its construction, I had to search for “Safety Island,” so named because at the time of the dam’s construction, it was an island in the road where workers could stand behind a berm to protect themselves from the never-ending onslaught of cement trucks.

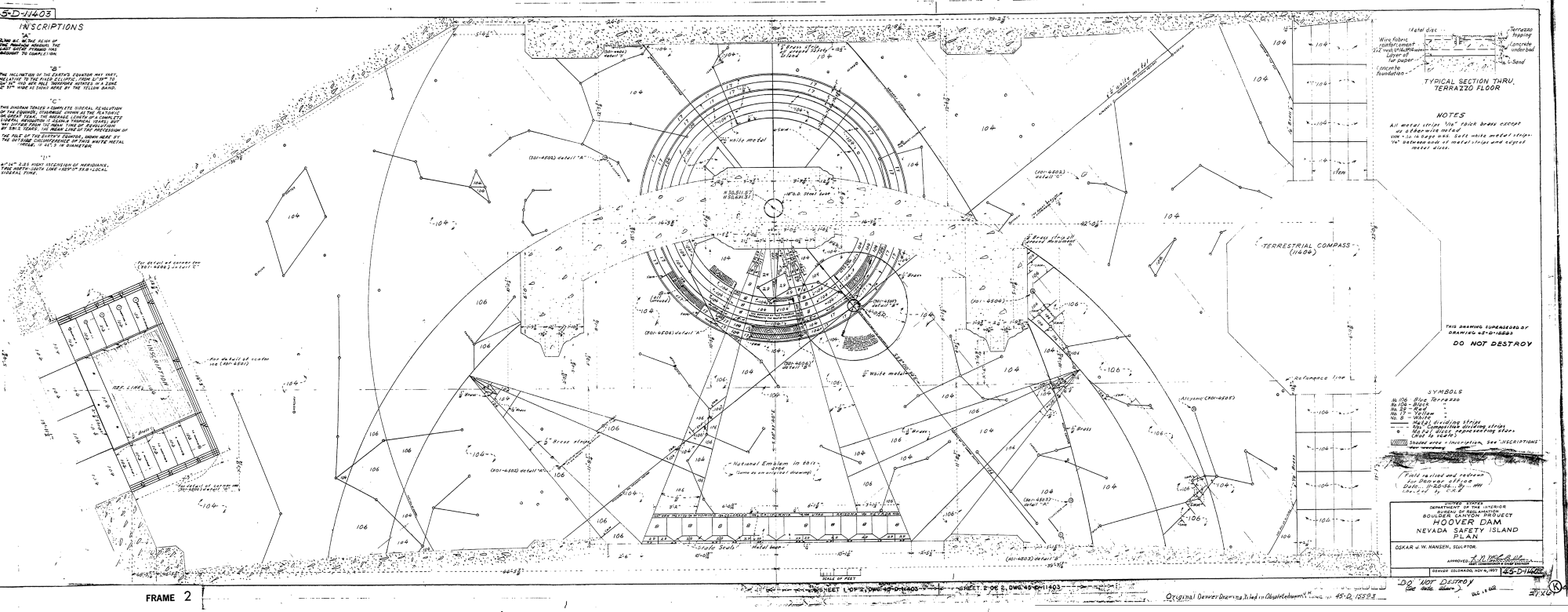
I now had some historical text and photos, but I was still missing a complete diagram of the plaza that would allow me to really understand it. I contacted the historian again, and she obtained permission from her superiors to release the actual building plans. I suspect that they generally don’t like to release technical plans of the dam for security reasons, but it seems they deemed my request a low security risk as the monument is not part of the structure of the dam. The historian sent me a tube full of large blueprints and a CD of the same prints already scanned. With this in hand I was finally able to re-construct the technical intent of the plaza and how it works.
In order to understand how the plaza marks the date of the dam’s construction in the nearly 26,000-year cycle of the earth’s precession, it is worth explaining what exactly axial precession is. In the simplest terms, it is the earth “wobbling” on its tilted axis like a gyroscope — but very, very slowly. This wobbling effectively moves what we see as the center point that stars appear to revolve around each evening.

Presently, this center point lies very close to the conveniently bright star Polaris. The reason we have historically paid so much attention to this celestial center, or North Star, is because it is the star that stays put all through the course of the night. Having this one fixed point in the sky is the foundation of all celestial navigation.

But that point near Polaris, which we call the North Star, is actually slowly moving and tracing a circle through the night sky. While Polaris is our North Star, Hansen’s terrazzo floor points out that the North Star of the ancient Egyptians, as they built the great pyramids, was Thuban. And in about 12,000 years, our North Star will be Vega. The workings of this precession are best explained with an animation, as in figure 1. Here you can see how the axis of the earth traces a circle in the sky over the course of 25,772 years.
Unfortunately it is a bit difficult to see how this all works in the inlaid floor at Monument Plaza. The view that you really want to have of the plaza is directly from above. You would need a crane to get this view of the real thing, but by using the original technical drawing as an underlay I was able to mark up a diagram which hopefully clarifies it (Fig. 2).

In this diagram, you can see that the center of the circle traced by the axial precession is actually the massive flag pole in the center of the plaza. This axial circle is prominently marked around the pole, and the angle of Polaris was depicted as precisely as possible to show where it would have been on the date of the dam’s opening. Hansen used the rest of the plaza floor to show the location of the planets visible that evening, and many of the bright stars that appear in the night sky at that location.
By combining planet locations with the angle of precession, we are able to pinpoint the time of the dam’s completion down to within a day. We are now designing a similar system — though with moving parts — in the dials of the 10,000 Year Clock. It is likely that at least major portions of the Hoover Dam will still be in place hundreds of thousands of years from now. Hopefully the Clock will still be ticking and Hansen’s terrazzo floor will still be there, even if it continues to baffle visitors.

I would like to thank Emme Woodward of the US Bureau of Reclamation for all her help in finding the original images and plans of Monument Plaza. If you have further interest in reading Hansen’s original writings about the plaza or in seeing the plans, I have uploaded all the scans to the Internet Archive.
Join our newsletter for the latest in long-term thinking
Subscribe