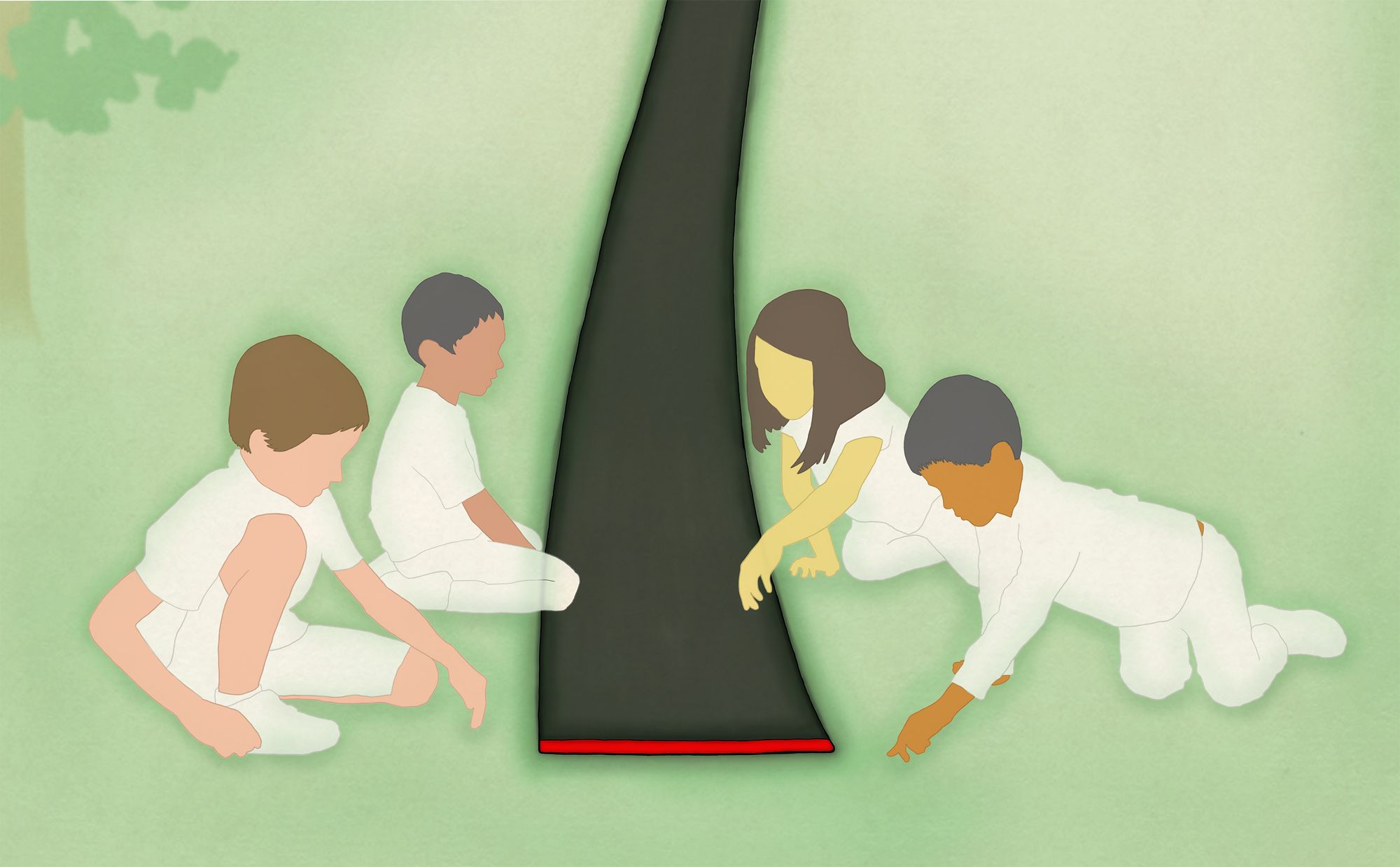
Five years ago, I worked briefly as an assistant in a Montessori elementary classroom. A few weeks into my time there I found myself on the playground, watching along with thirty silent children between the ages of nine and six as their teacher began to unroll a bolt of black fabric across the wood chips. “At first the earth was a fiery ball,” she said, “and this went on for a long time.” The fabric continued to unroll as she talked about volcanoes, rains, and cooling, and by the time the whole strip of fabric was laid out it was a hundred meters long, covering most of the playground. At the far end was one slender red line, which she told the students represented all of human history. This, she said, is how long it took the earth to be ready for the coming of the human being.
This lesson I witnessed, known now as the Black Strip, was first given more than seventy years before on the other side of the world. Italian doctor and educator Maria Montessori took what was supposed to be a six month training trip to India in 01939 after having found herself on the wrong side of the fascist powers of Europe. The Nazis had closed Germany’s Montessori schools and reportedly burned her in effigy. Mussolini, with whom she had originally collaborated, followed suit and closed Italy’s schools after Dr. Montessori, a pacifist, refused to order her teachers to take the fascist loyalty oath.
This seemingly opportune moment to leave Europe also came up against the moment when Italy entered World War II on the side of the Axis powers. As an Italian in India, Montessori was at the mercy of the British colonial government. They confined her to the grounds of her host organization — India’s Theosophical Society — and interned her adult son Mario, who had come along with her. Mario was eventually released and Montessori’s internment relaxed, but neither of them was permitted to leave India for the duration of the war. Their six month trip became seven years of training teachers and students in her methodology throughout India and Sri Lanka, and to this day a robust network of Montessori education remains in place there.
According to Montessori biographer Cristina De Stefano, it was during these seven years in India that Montessori developed much of what would become the natural history curriculum in her schools. The story behind the Black Strip I saw all those years later goes like this: some of Montessori’s Indian students considered their civilization superior to hers because it was older, one of the oldest in the world. In response, she devised a piece of black fabric three hundred meters long, spooled onto a dowel rod and unwound by a bicycle wheel down a village road somewhere near Kodaikanal. Montessori told her students that the black fabric (which has since been shortened by most Montessori schools for practical reasons) represented the fullness of geologic time on Earth, and that the line at the far end was the entire history of our species, Indian and Italian alike.
There’s no record of exactly how old these first students were, but current Montessori practice introduces the Black Strip along with what are known as The Great Lessons at the beginning of elementary school, where it is repeated each year so that by the time they are nine, students have seen the strip unroll three times.
Six years old might seem a bit early to introduce the depths of geologic time, but according to Alison Awes, the AMI Director of Elementary Training at the Montessori Center of Minnesota and the Director of Elementary Training at the Maria Montessori Institute in London, it’s exactly the right age. She notes that in Dr. Montessori’s scientific observations of children, “they were capable of so much more than what adults typically expected.” Elementary age children, Montessori noticed, possessed a strong capacity to reason, a drive to understand the world around them and how it functioned
Tracy Fortun, the teacher I worked for who rolled out the Black Strip on that day five years ago, tells me that the other elementary superpower that makes this the perfect age to introduce these concepts is a vivid imagination. Before her training, Fortun thought of imagination simply as fantasy, but she now sees it as a necessary tool for thinking about anything we can’t observe. “I have to use my imagination to think about five billion years,” she says.
Montessori lessons about natural history, like the Black Strip and the Clock of Eras (a poster of an analog clock in which the last 14 seconds represent humanity, presented once children are old enough to tell time), are not meant to deliver facts. Those, Fortun tells me, can come later. There is no scale of years to centimeters on the strip, nor are there many words spoken as it is rolled out. The lessons are impressionistic in order to engage the faculties of reason and imagination together and prompt a child’s own responses and questions, for which they can then seek answers. Awes tells me a story of a child who heard the third Great Lesson, The Coming of Human Beings, and then decided to sit down and make a list of every single thing he had done that day with his hands — tasks and capabilities unique to his species.
Each Montessori lesson involving the concept of deep time is a particular blend of these same components. There’s the Timeline of Life, in a sense the opposite of the Black Strip — it’s crammed with pictures of the different forms of life inhabiting each geologic era up to our own. Then there is the Hand Chart, similar to the Black Strip but with one picture on it: a hand holding a stone tool. On the Hand Chart the black expanse represents, instead of geologic time, all of human history before the invention of writing, and the small red line at the end contains the Bible, the Bhagavad Gita, everything any of us has ever written. “Human beings have been busy,” says Fortun to her students, “using their intelligence, using their hands, transforming their environment, taking care of each other, telling their stories, for all this time before anybody wrote anything down.”
And there is the BCE/CE timeline that uses a string teachers pull on both ends, to show that time is going in both directions and we can at once learn about the past and imagine the future. The ends of the string are frayed to demonstrate that time is still going, always. Awes tells me that she once saw a group of children take out the BCE/CE timeline and proceed to organize themselves along it as the historical figures they were currently studying. “It was this ‘aha’ moment of, ‘Hey, you and I are living and working at the same time, but you guys are 800 years before.’”
Given the impressionistic nature of the lessons and the student-led response to them, I ask how exactly teachers can tell that the concepts are really sinking in. The response they all give is that the full results can take years to see. Fortun says that long after they’ve moved out of her classroom, students will put together a project that astounds her, and when she asks where they got the idea they will say, “Remember what you showed us in second grade?”
Children, it turns out, need time to process and incorporate these expansive ideas. “Something really deep and important is happening,” Awes says of the seemingly fallow periods that can follow these lessons, “we just might not know what it is. And that’s where the adult has to get out of the way of the child. We can be obstacles, because we don’t give children enough time to reflect.”
Seth Webb, Director of School Services at the National Center for Montessori in the Public Sector, echoes this sentiment. “What schools need to do to allow for these concepts to be rooted in the hearts and souls of kids is to give them the time to explore them. I mean, if you want an appreciation of deep time, you have to give them the time to appreciate it deeply.”
What strikes me most is the faith these teachers seem to have in their students. To wait on children in this way requires immense trust, especially in the high-stakes years of a child’s education. It’s an attitude that stands in sharp contrast to the anxious system I remember growing up, a system constantly requiring evidence that children are indeed learning everything they must know. The question, I suppose, is what we consider most essential in preparing children for the world we are going to hand them. In a Montessori framework, one of the most central interdisciplinary goals is for children to grasp what Dr. Montessori calls the Cosmic Task — something shared by animate and inanimate earth alike. Awes puts it this way: “Each organism and inanimate object has a dual purpose. One of the purposes is to do what they do for survival, but while doing that they're giving something back.” So plants, for instance, remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in order to survive. But in doing that, what they give back to the rest of us is oxygen. There are lessons called “the work of wind” and “the work of water.” The universe and the earth are presented as a system of interdependence, developed over billions of years and honed with immense specificity to create the conditions under which life exists. Children who understand this, who are exposed to it repeatedly and given time to contemplate it, Awes tells me, start to wonder what their own Cosmic Task might be, how they might support their community and their future, how they might give back.

But how many children are even given the opportunity to wonder in this way? Maria Montessori began her work with some of Rome’s most underprivileged children, but now, in the U.S. at least, Montessori education is often seen as something of an elite luxury. In a widely read 02022 New Yorker review of De Stefano’s biography on Montessori, Jessica Winter noted that “there are only a few hundred public Montessori schools in the U.S.,” and that the Montessori method has been “routed disproportionately to rich white kids.”
Sara Suchman, the Executive Director of the National Center for Montessori in the Public Sector, paints a very different picture of Montessori in contemporary public education. In 02022 there were around 200,000 students receiving a Montessori education in nearly 600 U.S. public schools, she says, and more than half of them are Black, Indigenous, and People of Color. In a letter to the editor challenging Winter’s review, Suchman wrote that “there is nothing inherent in a Montessori classroom or school that makes it the unique domain of the wealthy.”
What is certainly true of these public Montessori schools, however, is that they tend to almost always be choice schools — open to all students in a school district regardless of address, but with an enrollment cap that means only a certain number can be admitted. Suchman cites Mira Debs’ Diverse Families, Desirable Schools (02019) to explain that over time more white, higher-income families proactively work the system to place their children in such schools. This problem is beyond the scope of the Montessori model itself, though presumably not beyond the scope of education policy in general.
“When a single model is serving 200,000 students, that both shows accomplishment and also opportunity,” Suchman tells me. One of the reasons Montessori education is worth our advocacy, according to Suchman, is that it is the model that best takes into account both the present and the future. “Kids are human beings right now, in this moment, and they need a positive experience right now…but they also need to be prepared. A lot of other methodologies will do one or the other, but Montessori does them together.”
Making Montessori more publicly accessible and therefore available to children in a wider economic range is a challenge for many reasons, but one that Suchman highlights strikes directly at the allowance for deep contemplation: the tension introduced by yearly testing, and our expectation of seeing constant, steady, measurable improvement. We don’t want to wait, and Montessori classrooms — which are multi-generational and span three grades — tend to demonstrate a burst of gains in each third year. For instance, when schools test yearly they will often see a plateau through first and second grade in Montessori schools instead of steady progress, which can cause anxiety if allowances aren't made for the fact that third grade is when much of the progress will manifest.
Educators must be prepared to accept a certain amount of waiting, to take a longer view and give kids some time.

Even outside of more public schools transitioning to a full Montessori model, there are opportunities for some of these concepts and methodologies for teaching natural history to make their way into all kinds of classrooms. Seth Webb sees the current moment as an opportunity for pedagogical cross pollination: “There are really amazing teachers everywhere, regardless of the overarching pedagogical foundation. We’ve moved into a new era where our pedagogy would do well to collaborate more.”
Children who have been given the Great Lessons and the time to appreciate the interdependence of our environment, the fragility and specificity and particularity of circumstances that allow for our existence, who know what it took for the earth to “be ready” for us, might be just the kind of people that we need right now. According to the Clock of Eras, it’s been 14 seconds, and we don’t know how many seconds more we have. So what will we do?
Maria Montessori believed that she was working at the end of the Adult Epoch, and that what was coming was the Epoch of the Child. It’s unclear precisely what she had in mind with that terminology, but it seems to speak of a time when children who are treated with sufficient respect and given sufficient time and resources become adults and alter, on a large scale, the way we carry out our lives. Crucially, however, nothing new like this can be ushered in without decisions made now, by those of us who are not yet citizens of any of these new possibilities. A cosmic task for us, perhaps.
I can imagine what it might look like, rolled out in front of me. These brief years of our unprecedented technological dominion I imagine a pale, sickly yellow, the color of the fear so many of my generation seem to carry — the fear that we have gone too far. And at the end, slender but frayed at the edges to connote its expansion, a full, deep, blue-tinted black of possibility like a bare night sky, like a beginning.
